

Looking at the official MySQL 8.0 Dockerfile I have a few concerns: FROM oraclelinux:7-slimĪRG MYSQL_SERVER_PACKAGE=mysql-community-server-minimal-8.0.23ĪRG MYSQL_SHELL_PACKAGE=mysql-shell-8.0.22 When the container spins up I need it to run: CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS my_db To conclude, we'll discuss the reliability of implementing databases in Docker production environments. Then we'll discover how data persistence is working across containers. In the first chapter, we'll cover the installation of a database on our local machine.
#Docker mysql drop database how to#
Ideally this would be passed in as a runtime argument so I could change it across runs if needed. Overview In this article, we'll review how to work with Docker to manage databases.
I'd like to be able to specify the directory on my machine where I want data stored and persisted across container runs. So its important to me that if there are any RDS MySQL 8.0 "tunings", configurations or optimizations that will be applied automatically, that my local MySQL container mimic those as much as possible to prevent the "works locally but not in dev" symptom from rearing its head.
#Docker mysql drop database software#
Locally I will run my software against this MySQL container, but non-locally I will be running my software on AWS against a MySQL 8.0 RDS cluster. I think if I uninstall mysql server from the host I'll be able to connect to the docker database, but surely there's a better approach.I'm trying to create a Dockerfile that will create an image that will have a MySQL 8.0 database on it. Nicholas $ mysql -h localhost -P 3306 -protocol=tcp -u root -p Yet that's not happening, I'm getting the host's database: nicholas $

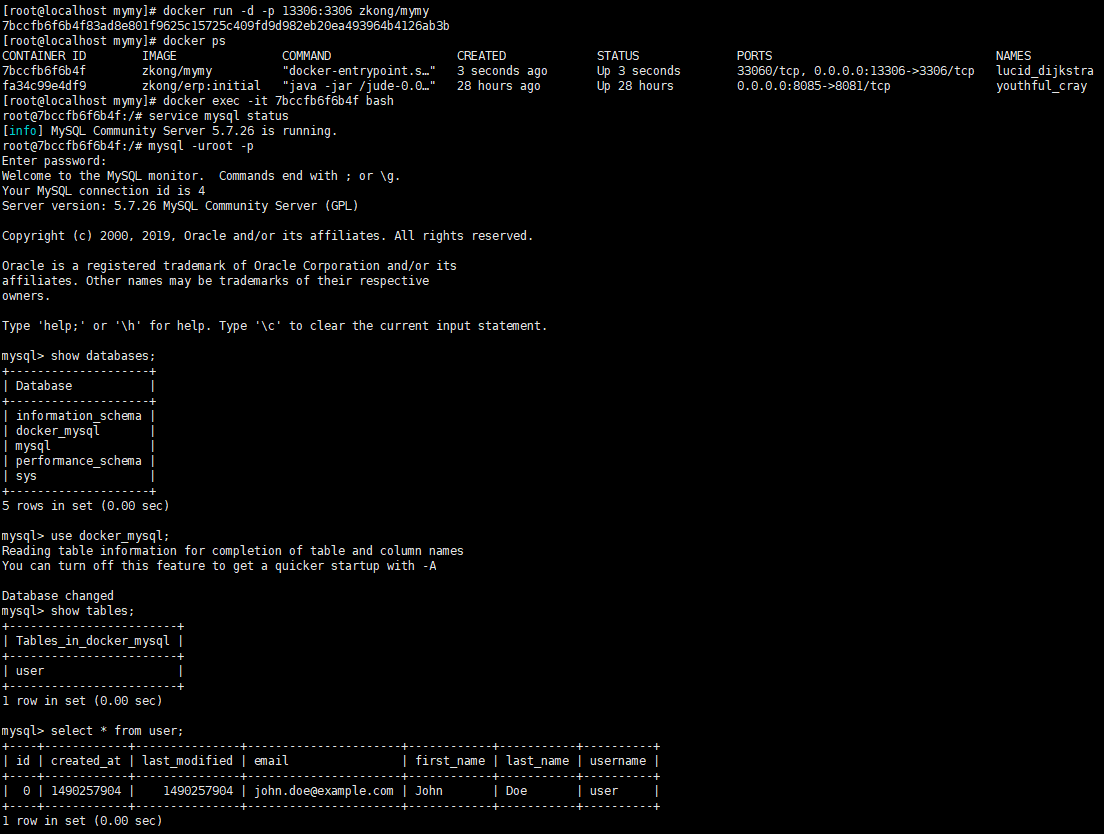
Root $ docker inspect mysql | grep passwordĪnd so I was expecting that by specifying tcp for localhost from the host I'd be able to connect to the docker container. Which is virgin, not having user user configured on the container. To do this, execute the next command: docker run -namemysql1 -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQLROOTPASSWORD123456 -d mysql/mysql-server:8.0. Set these variables to automatically provision a new empty database and user account: MYSQLDATABASE The name of a database schema to create when the server initializes for the first time. The next step is to run a container in Docker with the MySQL image. The MySQL Docker images support optional environment variables that let you manage the first-run database setup. Root $ docker exec -ti -user root mysql bash Automatically Creating A Database and User. I'm trying that explicit IP address because: root $Īlthough I'm also getting the same result for localhost in that I'm still logging into the host instance of MySQL rather than the container. If you don’t specify this, Docker will generate a random name. Here is what the second command line does: run Run a command in a new container. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. Then, use the following basic command to run a MySQL container: docker run -nametest-mysql mysql. Other names may be trademarks of their respective Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or itsĪffiliates. For a 'new project', we use now docker servers and one with a mysql 5.7 and a volume to save this new project database in a host folder, for exemple: /path/on/host/dockerise/db/ I want to backup too this new database. Server version: 8.0.21 MySQL Community Server - GPLĬopyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Trying to login to the container, but getting the host MySQL instance: nicholas $ Starting up the default mysql server: root $


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
